Is composting worth it? Many people ask this when looking for better ways to deal with waste. Composting turns food scraps and yard waste into rich soil that helps plants grow. It’s a smart alternative to sending waste to the landfill.
But composting takes time and effort. That’s why some people aren’t sure if it fits their lifestyle.
This article explains what composting involves. You’ll learn the benefits, the challenges, and some tips to get started. If you’re trying to improve your garden or reduce your trash, this guide will help you decide if composting is worth it.

What is Composting?
Composting is a way to turn things like food scraps, yard waste, kitchen waste, and other organic waste into good soil. You break down these things, and after some time, they become rich dirt. You can use this soil to help your garden or yard grow better. A lot of people like this because it is good for the earth and easy to do at home.
There are two main types: home and industrial. Home composting is good for people and small families. You can use a compost bin or pile to put kitchen scraps, dairy products, grass clippings, and other organic waste in it. Turning the pile often and keeping it damp will help make the decomposition process faster.
Industrial composting is run by big groups or city services. They deal with organic waste in larger amounts. They often take things like biodegradable plastics. These places control the conditions very closely. This helps the waste break down faster and fully.
Composting happens because of a natural process. Small living things, like bacteria and fungi, break down the organic matter. This makes heat, and the heat can get as high as 140 degrees Fahrenheit. The warm temperatures help it break down even faster. After a few weeks or sometimes months, you will get dark and crumbly compost. It will be ready to use in your garden.
Composting is a good way to deal with organic waste. It turns things you use every day into good soil. This can help both small and big jobs with using waste better.

Benefits of Composting
Environmental Impact
Composting helps lower the amount of waste that ends up in landfills. When you compost organic waste, it breaks down in a natural way. This process makes compost that is full of nutrients, and not harmful greenhouse gas like methane. By composting, you help decrease greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to a healthier environment.
Soil Health
Compost helps make healthy soil by giving it key nutrients. It also makes the soil better, so it can keep more water and not wash away so easily. Using compost helps grow more tiny things in the dirt that are important for plant growth. Adding two to four inches of soil compost can cut down on chemical fertilizers you may need, so your gardening can be better for the earth.
Cost-Effectiveness
Composting helps people save money on waste removal and on things for the garden. Instead of buying fertilizers from stores, you can use your own compost. It is easy to make from organic waste, garden waste, and egg shells. This way, you spend less and also turn waste into something useful for the garden.

Challenges of Composting
Composting can be good because it helps the earth in many ways. But, there are several challenges that can come up, which may stop people from starting. If you want to know more, read about these challenges here.
Time and Effort
Composting needs regular care to keep it working well. You have to turn the compost a lot so air can get in. You should check how wet it is often. If it is too dry or too wet, the pile will not break down right. A lot of hard work is needed to keep the right mix of brown materials and green ones. You need to keep this balance for the pile to break down like it should. With composting, you also have to wait several months before you get good compost to use. You need time and patience for this, but it can be worth it.
Space Requirement
Composting needs enough space to work well. The best place for this is a backyard or garden. But, not all people have that much outdoor space. A compost bin is smaller than a big pile, but it still needs some room. In cities, some people may not have enough space for even a compost bin. If there is not enough space, it can be hard for people to compost at all.
Potential Issues
If a compost pile is not handled well, it can start to smell bad. A pile that is not balanced will often make a strong odor. This can make people not want to keep working on it. Food scraps and the pile may also pull in pests like rodents or insects, if you do not manage it the right way. To help avoid these problems, you should bury your food scraps and cover your compost well, especially at the top of the pile. It can also help to think about the bottom of the pile when you set it up and manage it.
Local Regulations
Some places have rules that may stop or limit you from doing composting. A homeowners association or the local government might have rules for where you can compost and how you must do it. These rules could say you need to use certain containers or keep the compost a set distance from a property line. Before you begin, make sure to check with your local area and see what the rules are, so you follow them.
These challenges do not make composting impossible. But, to manage them well, you need to think about them and make a plan.
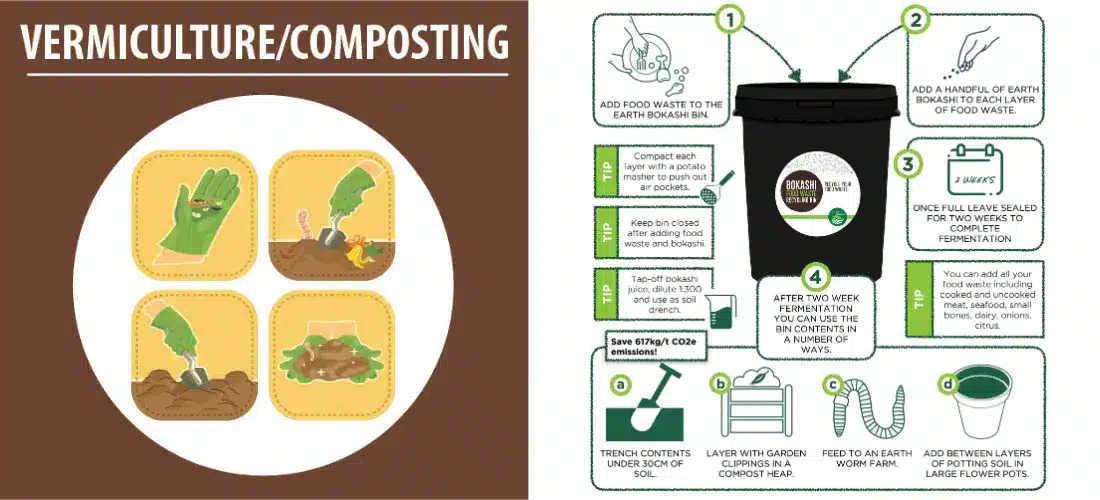
Detailed Composting Methods
There are many ways to do composting, so you can pick one that fits your life and space. Backyard composting is a common choice. In this method, people use compost bins or make heaps. You put in things like kitchen scraps and yard waste. Over time, these break down by themselves and turn into good soil to use in your garden.
Home composting is great because you can recycle what would be trash and get good soil for your plants. If you want something that works faster, try vermicomposting. To get started, you only need a pound of worms, usually red wigglers. They help speed up the decomposition process. This method uses little space and is a good choice if you live in an apartment or do not have much room. It is flexible, so people in many living situations can use it.
Another new way to deal with food waste is Bokashi composting. This method ferments food waste inside a closed container. You do not need much space to do this, and it can be set up indoors. That makes it a good choice for people living in the city. By looking into these composting options, you can find one that fits your needs. It will also help with your waste management in a good way.
Types of Home Composting
When the composting program is used, it helps lower methane emissions. This happens because it keeps organic waste, like food scraps, brown materials, yard waste, vegetable peels, and coffee grounds, out of landfills. Composting makes food scraps and other waste break down quickly with or without air, in a process called anaerobic decomposition. This helps improve soil health.
Composting puts nutrients back into the soil. Healthy soil helps plants grow strong and gives them what they need. This method supports different types of life in the ground and lets us use fewer chemical fertilizers. When you use the composting program, it sets up a cycle that is good for your garden or even big farms. Keeping up this simple practice over time will help all of us work towards a better and healthier world.
Steps for Effective Composting
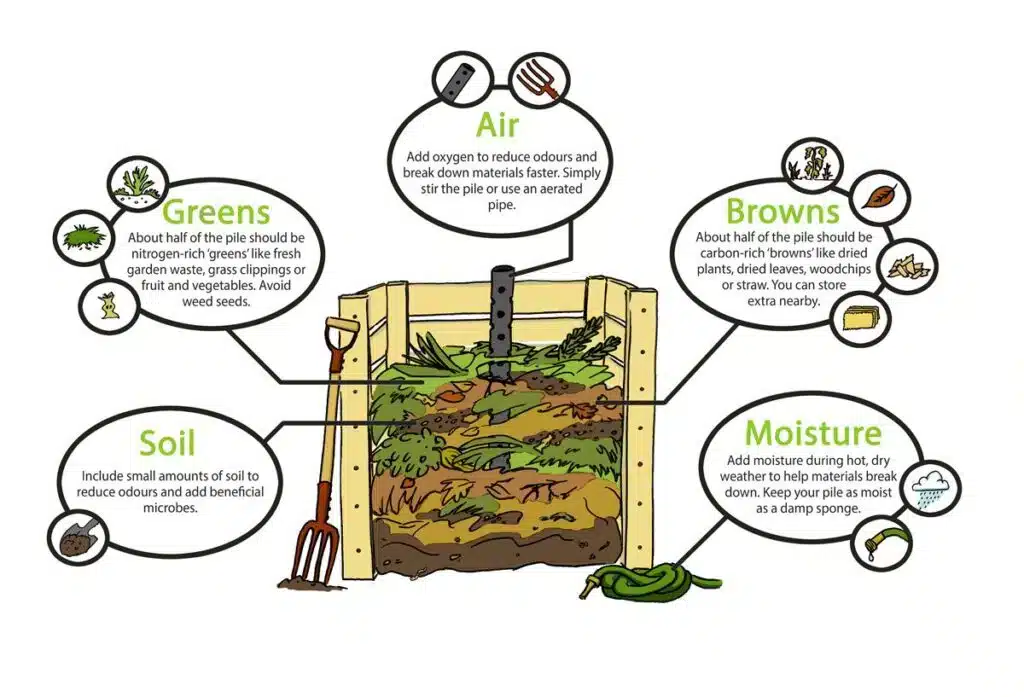
To get a good compost pile, you need to follow some simple steps. First, put down a base with things like twigs or straw. This helps air get into the pile. Then, add layers of green materials, for example, vegetable scraps, and brown materials, like dry leaves or paper. Try to use about two or three parts brown materials for every one part green. Watch out for anything like weed seeds that might end up in the mix. Keep an eye on the temperature of the pile, too. The right temperature will help the pile break down well.
Next, keep an eye on how wet your compost is. It should feel like a sponge that you have squeezed out. This means it is damp but not too wet. When you turn the pile often, you let air into it. This helps good bacteria grow and makes everything break down quicker. In a few months, when you see the compost looking dark and breaking into small pieces, it is ready for your garden. If you follow these steps, you can make rich compost to boost soil health and help plant growth.
Alternatives to Composting
If composting does not fit your daily routine, there are other good, eco-friendly waste solutions in the United States.
Dumpster Rental for Yard Waste:
Bargain Dumpster offers dumpsters that are made for yard waste. You can use these dumpsters to get rid of a lot of organic material when you finish big jobs in your yard. Renting one will help you clear out the debris fast. You do not have to worry about composting because the dumpster will do the job for you.
Municipal Yard Waste Programs:
Many cities have yard waste pickup or drop-off services. They take yard waste and other organic waste, then make it into mulch or compost. You can call or look online to see if your local waste management company has this. They can also tell you their rules and steps for using the service.
Other Sustainable Practices
Even if you do not have or use a compost, you can still handle your waste in the right way.
Vermiculture:
Vermiculture, or worm composting, means you use worms to break down organic waste. This is a good way to get rid of your food scraps and garden waste. People who do not have much space can use this method without any problem. Worm composting gives you a rich type of compost, and it does not take much time or hard work.
Bokashi:
Bokashi composting is a way to break down food waste inside your home by using fermentation. This type of composting does not need much space or take a lot of time. It can be a good fit for people who live in flats or places that have strict rules about composting.
By checking out these other options, you will be able to pick a waste management solution that is good for you and your way of life.

How to Get Started with Composting
Choosing the Right Method
Start by choosing a composting method that matches what you need. If you have an outdoor space, backyard composting can be a good choice. You can use a compost bin or make a simple pile for your organic waste. A garden fork is a useful tool to turn it over and keep things mixing well. If you do not have much space, try indoor composting. A countertop compost bin or a worm bin will work well in your home. This way, anyone can start turning food scraps and other waste into something good for the garden.
Backyard Composting
For people who are just starting out, it is good to use a simple bin with air holes. Be sure there is enough air and water can drain out. Turn the compost often to help things break down faster. Put in a mix of small pieces of green stuff like fruit scraps and brown materials like leaves for the best results.
Indoor Composting
If you live in an apartment or do not have much room, you can still compost inside. Countertop compost bins are small and easy to use. Worm bins, also known as vermicomposting, are another good way to compost indoors. These bins use worms to break down food scraps fast and in a good way.
Tips for Success
Balance the green and brown materials in your compost. Green materials are things like vegetable scraps. Brown materials are things like dead leaves and paper. Do not add meat, dairy, or oily foods to the compost. This helps stop bad smells and keeps pests away. Try to keep the compost moist. It should feel like a wrung-out sponge.
Bargain Dumpster Tip
If you have a lot of yard waste before you begin to compost, you can rent a dumpster from Bargain Dumpster. This will help you clear out the yard, so you have space to put your compost setup.
Conclusion
Composting is good for the environment and helps soil health. But, it takes time, effort, and needs to be managed the right way. Think about your own life and how much space you have before you start composting. If composting does not work for you, there are other ways to deal with waste. If you have a lot of waste to remove, like big piles of yard debris, you can use Bargain Dumpster for help. No matter if you go with composting or another option, it is important to handle waste the right way for a better, greener future.

